base address register|pci : Manila A signed offset or register is denoted by “+/−”, identifying that it is either a positive or negative offset from the base address register Rn. The base address register is a pointer . Bolehkah saya melihat keputusan 9 Lotto 4D dan 6D yang lepas? Ya, keputusan terdahulu 9 Lotto boleh dilihat di laman web rasmi dan GD4D. Pemain boleh mengakses data cabutan bersejarah untuk menganalisis trend dan membuat keputusan yang bermaklumat semasa memilih nombor.
PH0 · pci
PH1 · intel
PH2 · bios
PH3 · What is the Base Address Register (BAR) in PCIe?
PH4 · What Is Resizable BAR and How Do I Enable It?
PH5 · PCI configuration space
PH6 · How x86
PH7 · How does the Base Address Registers (BARs) in a PCI card work?
PH8 · Base Address Register
PH9 · 4.2. Base Address Registers
PH10 · 3.2. Base Address Register (BAR) Settings
Sa mga kababayan na gustong magbayad ng OWWA membership online kung kayo po ay nasa bakasyon or kahit nasa abroad ay pwede nio syang bayaran gamit ang GCash..
base address register*******The most important field in the "memory"-type bar is the 27-bit "Base Address" field, which determines the initial address in memory of the corresponding BAR region, in multiples of 16-bytes.pci A signed offset or register is denoted by “+/−”, identifying that it is either a positive or negative offset from the base address register Rn. The base address register is a pointer .To address a PCI device, it must be enabled by being mapped into the system's I/O port address space or memory-mapped address space. The system's firmware (e.g. BIOS) or the operating system program the Base Address Registers (commonly called BARs) to inform the device of its resources configuration by writing configuration commands to the PCI controller. Because all PCI devices are in an inactive state upon system reset, they will have no addresses assigned to the. I am trying to understand how the Base Address Registers (BARs) in a PCI card work, this is how I think they work: Each function in a PCI card have 6 BAR fields, . Resizable BAR (Base Address Register) is a PCIe capability. This is a mechanism that allows the PCIe device, such as a discrete graphics card, to negotiate .
Base Address Register (BAR) Settings. V-Series Avalon-MM DMA Interface for PCIe Solutions User Guide. Download PDF. View More. Document Table of Contents. 1. .A non-bursting 32-bit master with byte level byte enables. This type supports access to control and status registers. Note: If the Expansion ROM BAR of PF2 or PF3 is . It is the base register because it can be used in various based addressing modes: storing an address in BX, and an offset in SI or DI (the source and destination .Base address Registers (or BARs) can be used to hold memory addresses used by the device, or offsets for port addresses. Typically, memory address BARs need to be . All registers have to be the same size as each each other but don’t have to be the same as the processor mode. In particular, we can use 32-bit registers instead .
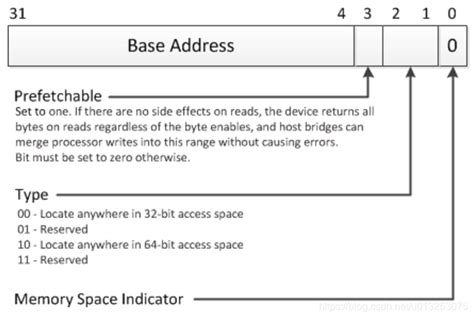
The most important field in the "memory"-type bar is the 27-bit "Base Address" field, which determines the initial address in memory of the corresponding BAR region, in multiples of 16-bytes.

A signed offset or register is denoted by “+/−”, identifying that it is either a positive or negative offset from the base address register Rn. The base address register is a pointer to a byte in memory, and the offset specifies a number of bytes.The system's firmware (e.g. BIOS) or the operating system program the Base Address Registers (commonly called BARs) to inform the device of its resources configuration by writing configuration commands to the PCI controller.
I am trying to understand how the Base Address Registers (BARs) in a PCI card work, this is how I think they work: Each function in a PCI card have 6 BAR fields, and each BAR field is 32-bit in size. Resizable BAR (Base Address Register) is a PCIe capability. This is a mechanism that allows the PCIe device, such as a discrete graphics card, to negotiate the BAR size to optimize system resources.Base Address Register (BAR) Settings. V-Series Avalon-MM DMA Interface for PCIe Solutions User Guide. Download PDF. View More. Document Table of Contents. 1. Datasheet 2. Getting Started with the Avalon-MM DMA 3. Parameter Settings 4. Registers 5. Error Handling 6. PCI Express Protocol Stack 7. V-Series Avalon-MM DMA for PCI .
A non-bursting 32-bit master with byte level byte enables. This type supports access to control and status registers. Note: If the Expansion ROM BAR of PF2 or PF3 is disabled, a memory read access to the BAR is responded to with 32'h0000_0000 indicating that the corresponding ROM BAR does not exist. It is the base register because it can be used in various based addressing modes: storing an address in BX, and an offset in SI or DI (the source and destination index registers respectively), allows memory to be accessed at BX + SI or BX + DI ( ibid, page 31), or BX + SI + immediate, or even BX + immediate.Base address Registers (or BARs) can be used to hold memory addresses used by the device, or offsets for port addresses. Typically, memory address BARs need to be located in physical ram while I/O space BARs can reside at any memory address (even beyond physical memory).
All registers have to be the same size as each each other but don’t have to be the same as the processor mode. In particular, we can use 32-bit registers instead of 64-bit ones by including the address prefix byte ( 0x67) in our encoding. “Scale-Index-Base-Displacement” addressing.
The most important field in the "memory"-type bar is the 27-bit "Base Address" field, which determines the initial address in memory of the corresponding BAR region, in multiples of 16-bytes.base address registerA signed offset or register is denoted by “+/−”, identifying that it is either a positive or negative offset from the base address register Rn. The base address register is a pointer to a byte in memory, and the offset specifies a number of bytes.The system's firmware (e.g. BIOS) or the operating system program the Base Address Registers (commonly called BARs) to inform the device of its resources configuration by writing configuration commands to the PCI controller.
I am trying to understand how the Base Address Registers (BARs) in a PCI card work, this is how I think they work: Each function in a PCI card have 6 BAR fields, and each BAR field is 32-bit in size.
Resizable BAR (Base Address Register) is a PCIe capability. This is a mechanism that allows the PCIe device, such as a discrete graphics card, to negotiate the BAR size to optimize system resources.Base Address Register (BAR) Settings. V-Series Avalon-MM DMA Interface for PCIe Solutions User Guide. Download PDF. View More. Document Table of Contents. 1. Datasheet 2. Getting Started with the Avalon-MM DMA 3. Parameter Settings 4. Registers 5. Error Handling 6. PCI Express Protocol Stack 7. V-Series Avalon-MM DMA for PCI .
A non-bursting 32-bit master with byte level byte enables. This type supports access to control and status registers. Note: If the Expansion ROM BAR of PF2 or PF3 is disabled, a memory read access to the BAR is responded to with 32'h0000_0000 indicating that the corresponding ROM BAR does not exist. It is the base register because it can be used in various based addressing modes: storing an address in BX, and an offset in SI or DI (the source and destination index registers respectively), allows memory to be accessed at BX + SI or BX + DI ( ibid, page 31), or BX + SI + immediate, or even BX + immediate.
Time Difference. Central Daylight Time is 1 hours behind Eastern Daylight Time and 10 hours and 30 minutes behind India Standard Time 8:00 am 08:00 in CDT is 9:00 am 09:00 in EDT and is 6:30 pm 18:30 in IST. CST to EST call time
base address register|pci